Actionable Guides and Tips for Successful
Offshoring to The Philippines
Cybersecurity Strategies for Offshore Operations

Cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, which makes safeguarding sensitive data crucial. If you’re doing business in the Philippines—particularly if you’re based in Australia, the US, or similar regions—you may face data security risks. The Philippines, as a major outsourcing hub, handles vast amounts of critical data daily, making it a potential target for hackers. While our previous blog covered Philippine data protection laws, securing this data is vital for maintaining your clients’ trust in your operations and protecting your company’s reputation. Partnering with trusted, ISO-certified providers like Shore360 helps protect your data against evolving threats.
There’s no denying offshoring introduces cybersecurity challenges—from managing remote teams to complying with both local and international data protection standards. To stay ahead of threats and minimise risks, organisations must implement robust security measures. Engaging with reputable offshore partners and adopting proactive cybersecurity strategies can create a secure environment for your operations.
Learn the essential cybersecurity strategies for offshore setups, break down the unique threats tied to offshoring, and gain actionable insights to protect sensitive data that we implement in our system for our clients.
Implementing Robust Cybersecurity Measures in Offshore Settings
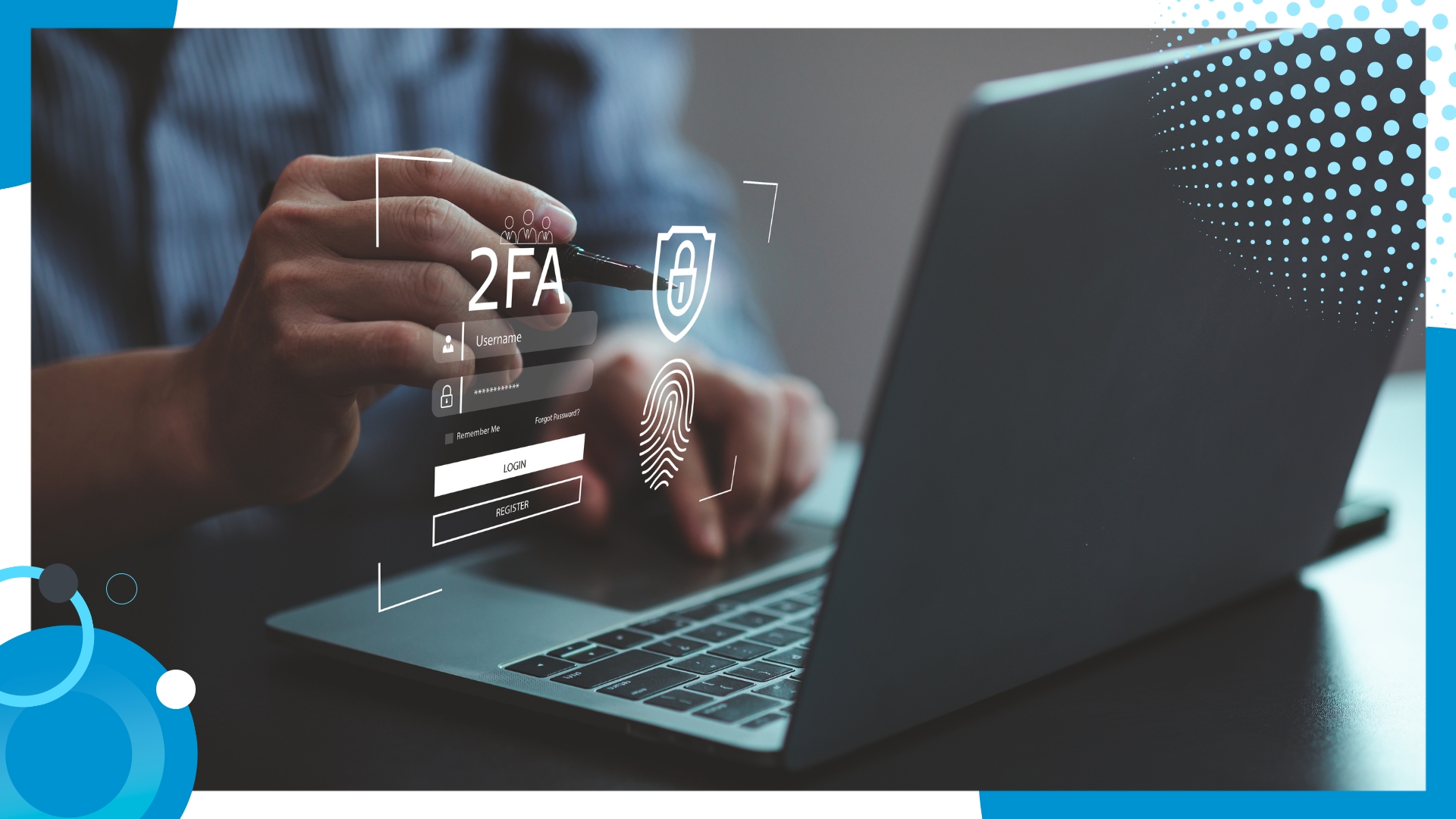

Securing offshore operations requires a multi-layered approach to protect sensitive data and systems from evolving cyber threats. For businesses offshoring to the Philippines—a region renowned for its thriving offshoring industry—implementing robust cybersecurity measures is non-negotiable. These steps ensure seamless, secure operations while maintaining client trust. Below are critical strategies to enhance cybersecurity in offshore settings that you can implement in your operations:
-
Adopt a Zero-Trust Security Model
“Always verify and just don’t trust” is the guiding concept of the zero-trust approach. Restricting access to sensitive systems and continuously validating user identities can help you minimise unauthorised access. This is especially important when managing remote offshore teams.
-
Use Advanced Encryption Techniques
Encryption protects sensitive data, keeping it secure during transmission and storage. Ensure you implement end-to-end encryption protocols for all communications and data exchanges with your offshore teams.
-
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds an extra security layer by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods—like passwords, biometrics, or authentication apps. This is crucial for your offshore employees who are accessing your systems from different locations.
-
Implement Network Segmentation
Dividing networks into smaller, isolated segments limits the spread of cyberattacks. Restricting access to specific network areas can better protect critical systems and data if a breach occurs. You can consult your offshoring provider if they have these capabilities so you can implement them in your operations.
-
Secure Remote Work Environments
Many offshore employees work remotely, and this exposes your data to added cyber risks. To counter this, make sure you use virtual private networks (VPNs), endpoint security tools, and secure Wi-Fi connections for all remote access—tools that many trusted offshoring partners already provide to keep your data safe.
-
Conduct Regular Security Audits
Frequent audits identify vulnerabilities in the IT infrastructure and help businesses address them before cybercriminals can exploit them. Regular penetration testing is also recommended to test the resilience of offshore systems.
It is essential to ensure that your offshore provider conducts annual “penetration testing” to identify and address potential vulnerabilities in their systems. Additionally, partnering with a provider that works with a third-party data security auditor and adheres to global security standards and tools strengthens the overall security framework. This process ensures that your sensitive data remains protected, maintaining the integrity of your operations and safeguarding against cyber threats.
Key Cybersecurity Threats in Offshoring
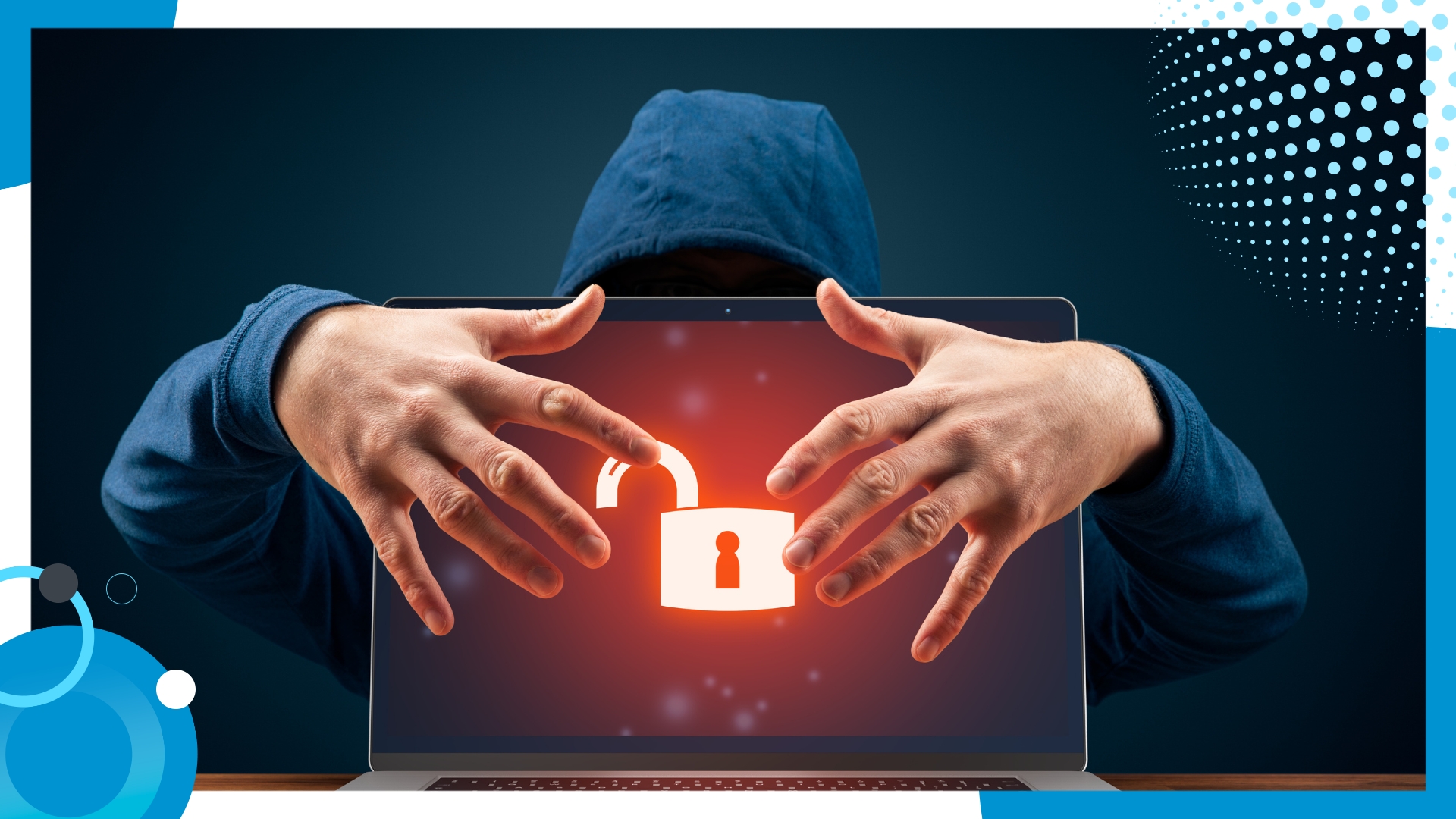

We’ve established that offshoring can introduce unique cybersecurity challenges that businesses must address, and now you’re aware of the preventive measures you can implement. To deepen your understanding, here are some of the cybersecurity threats that may or may not affect your offshore operations in the Philippines:
-
Insider Threats
Employees or contractors with malicious intent—or even those who make unintentional errors—can pose significant risks, especially if you engage freelancers who may not be fully compliant with regulations. In offshoring operations where access to sensitive data is often necessary, it’s crucial to implement strict user access controls and conduct regular employee training to minimise these risks. Working with an experienced offshoring provider can help you establish these safeguards, ensuring that proper access is granted only to authorised personnel and that all team members are aware of best practices for maintaining data security.
-
Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a common method cybercriminals use to steal data, particularly targeting offshore employees in customer-facing roles. To prevent this, it’s essential to train staff to recognise phishing attempts and follow security protocols. Regular training updates, email filtering systems, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) add extra layers of protection. Offshoring providers can support this by conducting security audits, running phishing simulations, and ensuring that your offshore staff are equipped to detect and report suspicious emails promptly.
-
Ransomware Attacks
Ransomware attacks, where cybercriminals encrypt data and demand payment for its release, are an increasing threat. These attacks can disrupt offshore operations that rely on continuous access to critical systems and data.
-
Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Offshore outsourcing often involves third-party vendors, which can create additional vulnerabilities in the supply chain. A breach in one vendor’s system can compromise the entire network, affecting both the offshore partner and the client company.
-
Data Exfiltration
Cybercriminals may target offshore operations to extract sensitive data, including customer information, intellectual property, or financial records. This is especially concerning for industries like healthcare, finance, and e-commerce, where privacy and compliance are critical.
-
Weak Endpoint Security
Offshore employees often use personal devices or home networks, which may lack robust security measures. These endpoints are prime targets for hackers seeking to infiltrate company systems.
Best Practices for Protecting Sensitive Data

We’ve discussed how businesses must adopt proactive measures to prevent cyberattacks and the common threats faced in offshoring, especially when it comes to data security. Now, it’s crucial to understand the best practices that align with these preventive strategies to effectively counter emerging threats. Here are key best practices:
Enforce a Strict Data Access Policy
Implement a least privilege access model, ensuring that offshore employees have access only to the data and systems necessary for their specific roles. Role-based access control (RBAC) helps minimise the risk of unauthorised access.
Regular Employee Training and Cybersecurity Awareness
One of the largest cybersecurity weaknesses is still human error. To mitigate this, regularly conducting cybersecurity training sessions for your offshore teams is essential. Focus areas should include:
- Recognising phishing attacks
- Secure handling of sensitive data
- Password management best practices
- Social engineering awareness
Adopt a Zero-Trust Security Architecture
Zero-trust frameworks require continuous identity verification before granting access to any system, greatly reducing the risk of insider threats and unauthorised access. Implementing this approach allows you to create a checklist where offshore staff have specific access to specific data, making it easier to pinpoint issues when they arise and enhance overall security.
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Strong Password Policies
Require employees to use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) for system logins and enforce strong password policies. This should include regular password changes, the use of complex combinations, and the implementation of password managers to further enhance security.
Encrypt Data at Rest and in Transit
Use end-to-end encryption to protect sensitive data from unauthorised access. Ensure that:
- Emails and file transfers are encrypted.
- Databases storing confidential information are secured with AES-256 encryption.
- Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols are used for all internet communications.
Deploy Endpoint Security Solutions
Offshore employees often work remotely or use personal devices, increasing security risks. Implement:
- Enterprise-grade antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Remote device management (MDM) solutions to monitor and control access.
- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) to secure internet connections.
Establish a Robust Incident Response Plan
No cybersecurity strategy is complete without a well-documented incident response plan. This should include:
- A clear escalation process in case of a breach.
- Immediate containment and mitigation protocols.
- Regular penetration testing and cybersecurity drills to assess the effectiveness of response measures.
Ensure Compliance with Local and International Data Protection Laws
In addition to adhering to the Philippines’ Data Privacy Act (DPA) of 2012, businesses must also comply with relevant international standards, including:
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) for EU-related data processing.
- ISO 27001:2022 certification for information security management.
- HIPAA Compliance for offshore operations handling healthcare data.
Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing
Conducting frequent cybersecurity audits and penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Offshore outsourcing providers should undergo periodic assessments to ensure they remain compliant with best security practices, safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring continuous protection against evolving cyber threats.
Secure Data Backups and Business Continuity Plans
Regular automated backups should be performed and stored in secure, offsite locations to ensure quick recovery in case of a cyberattack. Additionally, data security should be part of your offshore business continuity plan to minimise downtime and business disruptions, ensuring your offshore operations can resume smoothly after an incident.
When you choose to offshore with a partner like Shore360, an ISO 27001:2022-certified company, you can seamlessly implement your current software system into their operations. With their support, you’ll also benefit from diagnostics and ongoing security assessments. Shore360 conducts annual data security audits with a trusted third-party auditor to ensure that all equipment used by offshore staff remains free from vulnerabilities, guaranteeing smooth and secure operations. This proactive approach to data security helps safeguard your business and ensures compliance with the highest standards of information security.
Conclusion

As offshore outsourcing grows, so do the cybersecurity risks associated with handling sensitive data across borders. Businesses offshoring to the Philippines must adopt a proactive approach to securing their operations. This includes implementing robust cybersecurity measures, staying vigilant against evolving threats, and adhering to best practices for data protection.
Cybersecurity is not just a technical necessity but a strategic investment in business continuity, client trust, and long-term success in your offshoring journey. Constantly preparing for any cyber threats and continuously refining security protocols can help any business maximise the benefits of offshoring while maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture.
Partner with Shore360 for secure offshoring in the Philippines!